Mr JGB: Bank of Japan Could Achieve Inflation Target Through Labor Shortage
Background
Michio Saito, also known as Mr JGB, believes that the Bank of Japan may hit its stable inflation target this year, but not in the traditional way. Instead of strong demand driving up wages and prices, Saito suggests that the chronic labor shortage in Japan will be the main contributing factor.
Analysis
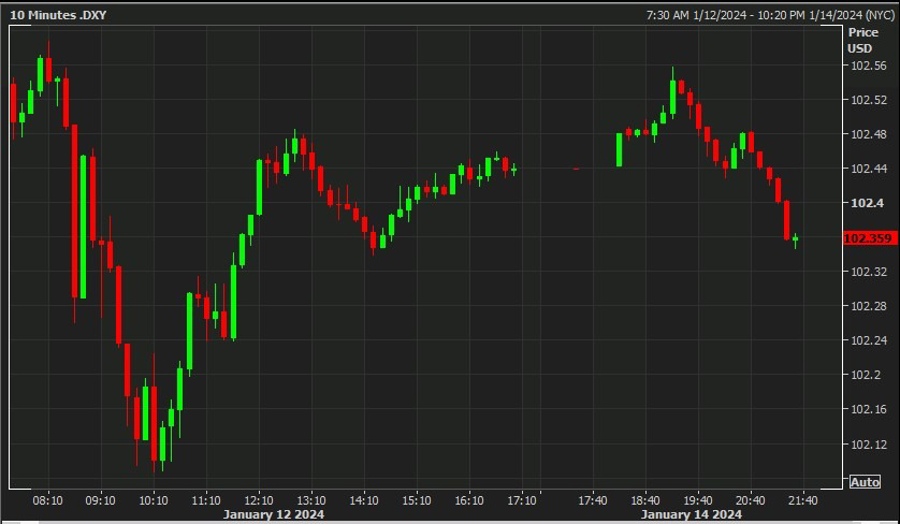
In a recent report from Bloomberg, Saito predicts that Japanese long-term yields will remain relatively stable, hovering around 1%. This is regardless of any potential changes to the Bank of Japan’s yield curve control program or short-term policy rates.
Saito’s theory challenges the central bank’s conventional wisdom and offers a unique perspective on Japan’s economic landscape. By emphasizing the impact of labor shortages on inflation, he provides a compelling argument for why traditional economic models may need to be reevaluated.
Impact on Individuals
According to experts, Saito’s predictions could have a significant impact on individuals in Japan. If the Bank of Japan does manage to achieve its inflation target through labor shortage-driven price increases, it may lead to higher costs of living for ordinary citizens. This could result in decreased purchasing power and potentially impact overall quality of life.
Global Implications
On a global scale, Mr JGB’s analysis could provide valuable insights into how labor shortages affect inflation in other countries. By highlighting the role of workforce dynamics in economic growth, Saito’s theory may prompt policymakers worldwide to reconsider their strategies for achieving stable inflation rates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Michio Saito’s unconventional stance on Japan’s inflation target challenges traditional economic thinking and offers a fresh perspective on the role of labor shortages in driving price increases. Whether his predictions come to fruition or not, Saito’s insights are a reminder of the complex interplay between labor markets, inflation, and economic policy.