The Central Bank of the Republic of China (Taiwan) and Intervention Threats
Understanding the Central Bank’s Role
The Central Bank of the Republic of China (Taiwan) recently announced its intention to intervene in the foreign exchange market in order to prevent dramatic fluctuations of the Taiwan dollar against the US dollar. This move is aimed at maintaining stability in the currency market and ensuring that the Taiwan dollar remains competitive in the global economy.
Intervention Strategy
The Central Bank stated that it will sell US dollars to smooth the market, as the value of the Taiwan dollar is largely determined by supply and demand dynamics. By stepping in to stabilize the currency, the Central Bank hopes to prevent any sharp depreciation that could harm Taiwan’s economy.
Inflation Outlook
The Central Bank also highlighted Taiwan’s stable inflation outlook compared to other countries. It emphasized that if oil prices were to hit $100 per barrel, this could delay the easing of inflation for major economies, including Taiwan. This is an important factor to consider when assessing the potential impact of external economic events on Taiwan’s economy.
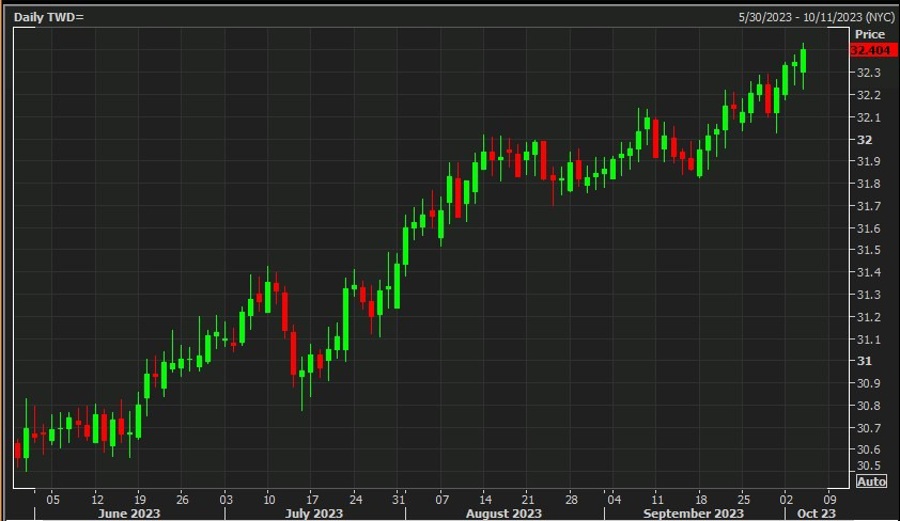
USD/TWD Daily Candles
Analysts have been closely monitoring the USD/TWD daily candles, which have been showing a persistent slide for the Taiwan dollar. While this trend is not unique to Taiwan and is influenced by global market factors, the Central Bank’s intervention efforts are aimed at mitigating any adverse effects on the country’s currency.
Impact on Individuals
Individuals in Taiwan may experience more stable currency exchange rates and reduced volatility in the foreign exchange market as a result of the Central Bank’s intervention. This could potentially benefit importers, exporters, and individuals who engage in international transactions.
Impact on the World
On a global scale, the Central Bank of the Republic of China’s intervention in the currency market could have ripple effects on other economies. By stabilizing the Taiwan dollar and preventing excessive fluctuations, Taiwan’s actions may contribute to overall market stability and confidence in the global economy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Central Bank of the Republic of China’s intervention threats reflect its commitment to maintaining stability in the currency market and safeguarding Taiwan’s economy against external shocks. By closely monitoring inflation trends and global market developments, the Central Bank is taking proactive measures to ensure the resilience of the Taiwan dollar in the face of uncertainty.