Understanding Soc Gen’s Forecast on the Sliding Yuan
Market Enthusiasm Fizzles Out
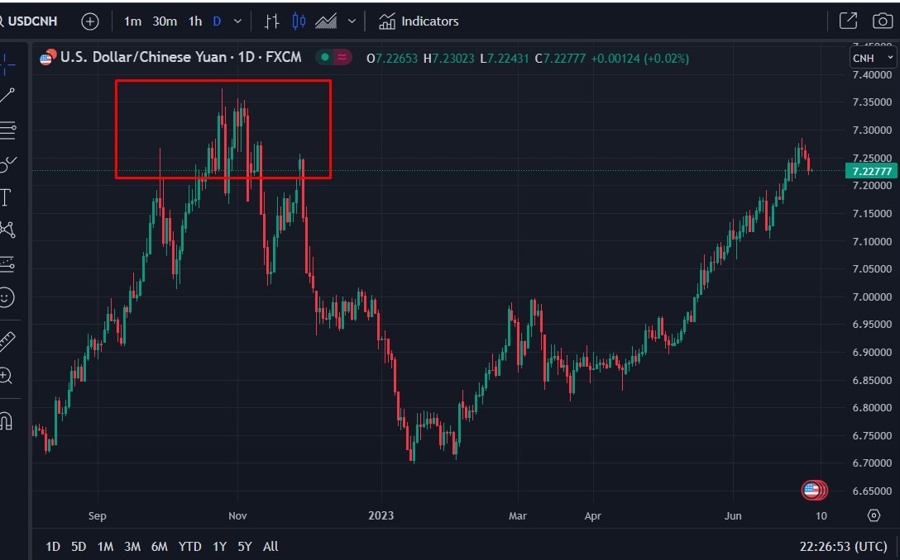
Societe Generale (Soc Gen) has recently predicted that the USD/CNY exchange rate will reach 7.30 in the third quarter of this year and rise to 7.40 by the first quarter of 2024. This forecast comes as the market’s initial enthusiasm about China’s reopening post-pandemic has started to wane. Despite some positive indicators, the underlying structural issues in the Chinese economy have become more prominent, causing investors to focus more on the challenges ahead rather than the short-term recovery.
Yuan Weakening Further
According to Soc Gen, the combination of market skepticism and China’s structural issues is likely to lead to a continued weakening of the yuan. Surprisingly, the People’s Bank of China (PBoC) does not appear overly concerned about the currency’s decline. This lack of intervention from the central bank suggests that the depreciation of the yuan may be part of a broader strategy to address economic challenges.
Impact on Individuals
As the yuan weakens against the US dollar, individuals may notice changes in the cost of imported goods and overseas travel. Exchange rate fluctuations can affect purchasing power and potentially lead to higher prices for foreign goods and services.
Global Implications
The depreciation of the yuan could have significant implications for global trade and financial markets. A weaker Chinese currency may make Chinese exports more competitive on the international stage, potentially leading to trade imbalances and tensions with other countries. Additionally, fluctuations in the USD/CNY exchange rate can impact global foreign exchange markets and investor sentiment.
Conclusion
Overall, Soc Gen’s forecast on the sliding yuan highlights the complex economic dynamics at play in China and the broader global economy. As the yuan continues to weaken, individuals and businesses will need to closely monitor exchange rate movements and adjust their financial strategies accordingly. The implications of a depreciating yuan extend beyond China’s borders and could have lasting effects on global trade and financial stability.